| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
A Micromachined Geometric Moiré Interferometric
Floating-Element Shear Stress Sensor
+ Download |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
MEMS Direct Shear Stress Sensors
- Direct Measurement Techniques
- Thermal Type Measurements
- Characterization Methods
The shear stress sensors located within the cluster consists of two sensing elements. First, there's the actual shear sensor, which is located in the center of figure 1. It is a Silicon Nitride element placed over the top membrane of an evacuated cavity. The evacuated cavity serves to thermally isolate the sensing element from any changing temperatures within the substrate.
The shear sensor is considered a thermal type shear sensor. It is located on one arm of a constant temperature bridge. As fluid velocity (and hence shear stress) increase, heat loss across the sensor increases. This phenomenon results in the constant temperature bridge creating a high voltage drop across the sensor arm of the bridge. This measurable increase is proportional to an increase in shear stress.
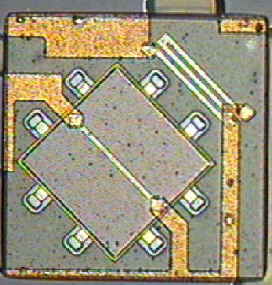
Figure 1. Shear Stress Sensor
The "S" shaped element located in the upper-right-hand corner of figure 1 is a temperature sensitive resistor. This resistor serves as the other element on the sensor arm in the Wheatstone bridge. When the temperature changes across the sensor during measurements this element provides temperature compensation.
As with the other MEMS sensors this temperature compensation is critical. In previous experiments temperature changes introduced large amounts of error if left unaccounted for. However, when correctly accounted for this sensor proved to be extremely accurate. This fact was demonstrated in the September 2000 tunnel test.
|