| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Development of Doppler Global Velocimetry as a Flow Diagnostics Tool
+ Download
Three Component Doppler Global Velocimeter Measurements of the Flow Above a Delta Wing
+ Download
Doppler Global Velocimeter Measurements of the Vortical Flow Above A Thin Delta Wing
+ Download
Doppler Global Velocimetry - A New Way to Look at Velocity
+ Download
Assessing the Capability of Dopplar Global Velocimetry to Measure Vortical Flow Fields
+ Download
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Doppler Global Velocimetry (DGV)
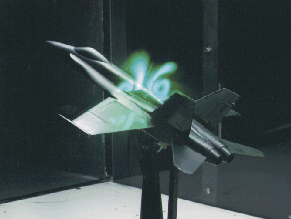 DGV is a non-intrusive measurement technology that can provide global, multi- or single- point velocity measurements. The technology can provide three-component velocity measurements at video rates (global), or greater than 100 kHz sample rates (point). DGV is a non-intrusive measurement technology that can provide global, multi- or single- point velocity measurements. The technology can provide three-component velocity measurements at video rates (global), or greater than 100 kHz sample rates (point).
The technology does not require resolution of individual particles, nor is it a single particle per measurement method. Average of optical frequency, not Doppler frequency. Doppler Global Velocimetry Test
Instantaneous global measurements can be obtained using a Nd:YAG laser. Continuous point measurements can be obtained with Argon ion or CW nd:YAG lasers (Iodine) or laser diodes (Cesium).
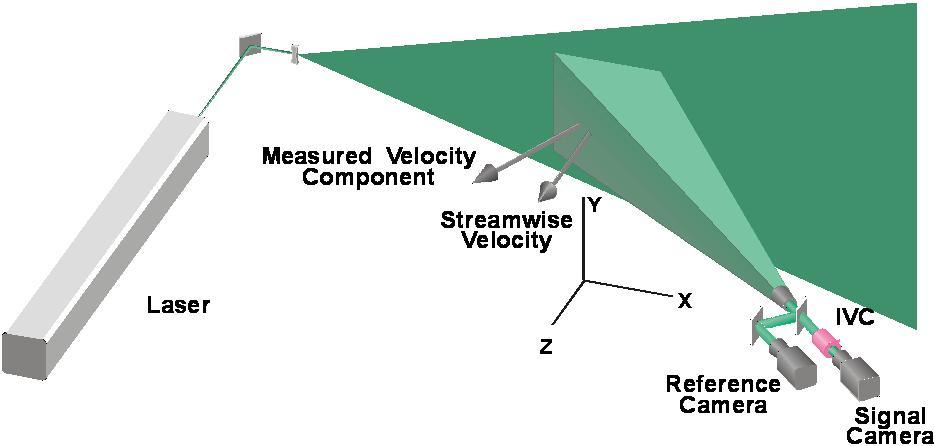
DGV Optical Configuration:
Typical Accuracy:
The typical accuracy of Doppler Global Velocimetry is 5%.
Requirements:
- Multiple Optical Access
- Seeding
- Image Processing
Primary Limitations of Doppler Global Velocimetry:
Primary Advantages of Doppler Global Velocimetry:
- Planar
- Simultaneous Three Components
|




